File read and write
f you are familiar with file reading and writing in standard C language, you can read and write files in standard C language.
For some commonly used file read and write operations, we made a simple package based on the C language file read and write interface, which is convenient to use. If necessary, you can follow the steps to integrate the source code into your own project.
/**
* Write a file, if the file exists, it will be overwritten, if the file does not exist, create a new file and write the content
* Return true if successful
*/
bool WriteFile(const char* filename, const void* data, int len);
/**
* Append content at the end of the file, if the file does not exist, create a new file first, and then write the content
* Return true if successful
*/
bool AppendFile(const char* filename, const void* data, int len);
/**
* 读文件
* Read file
* Success, save the file in the data of string in binary form, read the binary content with string.data()
* Return an empty string on failure
*/
string ReadFile(const char* filename);
Porting steps
Create a new folder under the jni folder of the project and name it
io
Downoad ioutil.h 、ioutil.cpp Two files, save them in the
iofolder.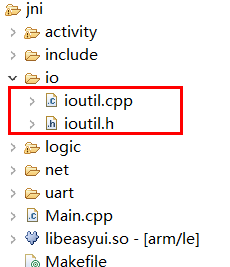
How to use
- Introduce header files
#include "io/ioutil.h" Write file
//Write the string "0123456789" into the file 123.txt const char* filename = "/mnt/extsd/123.txt"; //The path where the file is saved const char* str = "0123456789"; ioutil::WriteFile(filename, str, strlen(str));Additional files
//Append the content to the end of the file, if the specified file does not exist, create a new file. const char* append_str = "abcdefgh"; ioutil::AppendFile(filename, append_str, strlen(append_str));Read file
const char* filename = "/mnt/extsd/123.txt"; //Read all the contents of the file and save it in content string content = ioutil::ReadFile(filename); //Output each byte read to the log in hexadecimal for (size_t i = 0 ; i < content.size(); ++i) { LOGD("第%02d字节=0x%02X", i, content.data()[i]); }[!Warning] The
ioutil::ReadFilefunction reads all the contents of the file into the memory. If the specified file is too large, it will cause insufficient memory and may cause an exception.
Write files continuously, suitable for writing large files
const char* filename = "/mnt/extsd/123.txt"; const char* append_str = "abcdefgh"; ioutil::Writer w; if (w.Open(filename, false)) { for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { w.Write(append_str, strlen(append_str)); w.Write("\n", 1); } w.Close(); }Continuous reading, suitable for processing large files
const char* filename = "/mnt/extsd/123.txt"; ioutil::Reader r; if (r.Open(filename)) { char buf[1024] = {0}; while (true) { int n = r.Read(buf, sizeof(buf)); if (n > 0) { //There is read content, output every byte for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { LOGD("%02x", buf[i]); } } else if (n == 0) { //End of reading file break; } else { //Error break; } } r.Close(); }
Test code
/**
* Triggered when the interface is constructed
*/
static void onUI_init() {
//Write file
const char* filename = "/mnt/extsd/123.txt";
const char* str = "0123456789";
ioutil::WriteFile(filename, str, strlen(str));
string content = ioutil::ReadFile(filename);
LOGD("Read bytes%d, content:%s", content.size(), content.c_str());
//Append file
const char* append_str = "abcdefgh";
ioutil::AppendFile(filename, append_str, strlen(append_str));
content = ioutil::ReadFile(filename);
LOGD("Read bytes%d, content:%s", content.size(), content.c_str());
ioutil::Writer w;
if (w.Open(filename, false)) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
w.Write(append_str, strlen(append_str));
w.Write("\n", 1);
}
}
w.Close();
ioutil::Reader r;
if (r.Open(filename)) {
char buf[1024] = { 0 };
while (true) {
int n = r.Read(buf, sizeof(buf));
if (n > 0) {
//There is read content, output every byte
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
LOGD("%02x", buf[i]);
}
} else if (n == 0) {
//End of reading file
break;
} else {
//Error
break;
}
}
r.Close();
}
content = ioutil::ReadFile(filename);
LOGD("Read bytes%d, content:%s", content.size(), content.c_str());
//If it is a read binary file, not text, you should get the binary like this
//Output each byte in hexadecimal
for (size_t i = 0; i < content.size(); ++i) {
LOGD("%02d byte=0x%02X", i, content.data()[i]);
}
}